Follicular Epithelial Cell Hypertrophy Induced by Chronic Oral
By A Mystery Man Writer
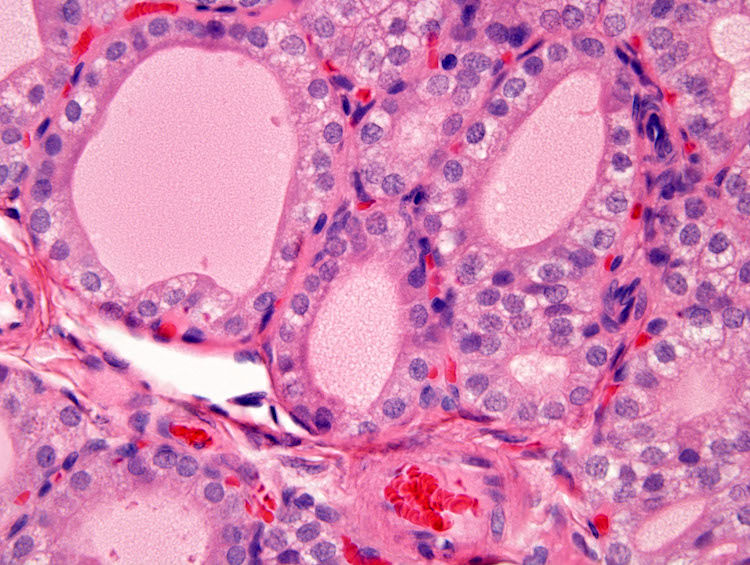
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) affects the thyroid morphologically and/or functionally in adult animals. Recently, the National Toxicology Program conducted a 2-year gavage study of TCDD in female Harlan Sprague–Dawley rats. The only treatment-related alterations found in thyroid follicles were decreased luminal size and increased height of the follicular epithelial cells, without prominent protrusion into the lumen.

Thyroid Gland, Follicle, Epithelium - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas
IJMS, Free Full-Text

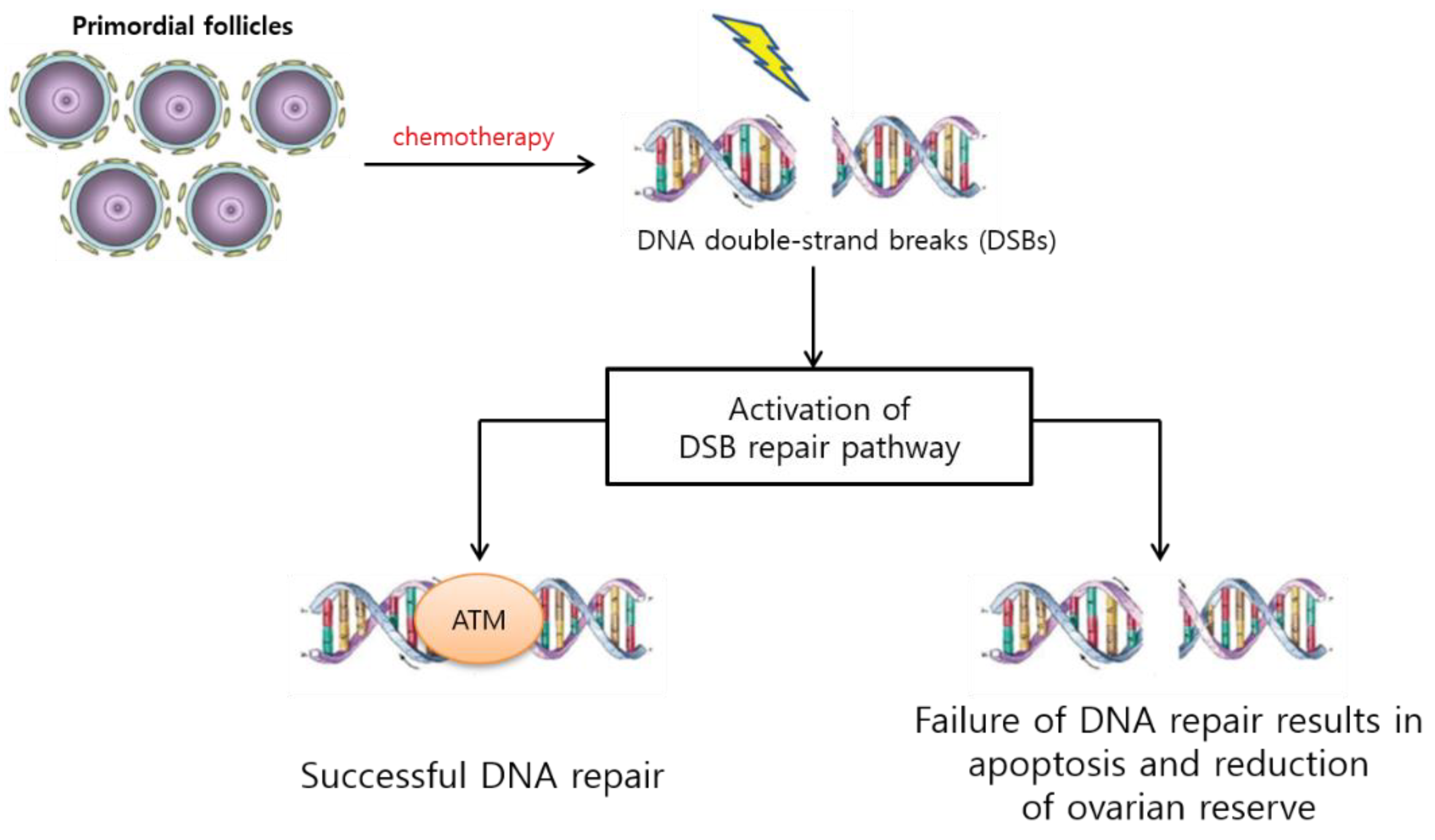
The sectional epithelial height (SEH) of follicles in thyroids of

Follicular Epithelial Cell Hypertrophy Induced by Chronic Oral Administration of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin in Female Harlan Sprague–Dawley Rats - Toxicologic Pathology
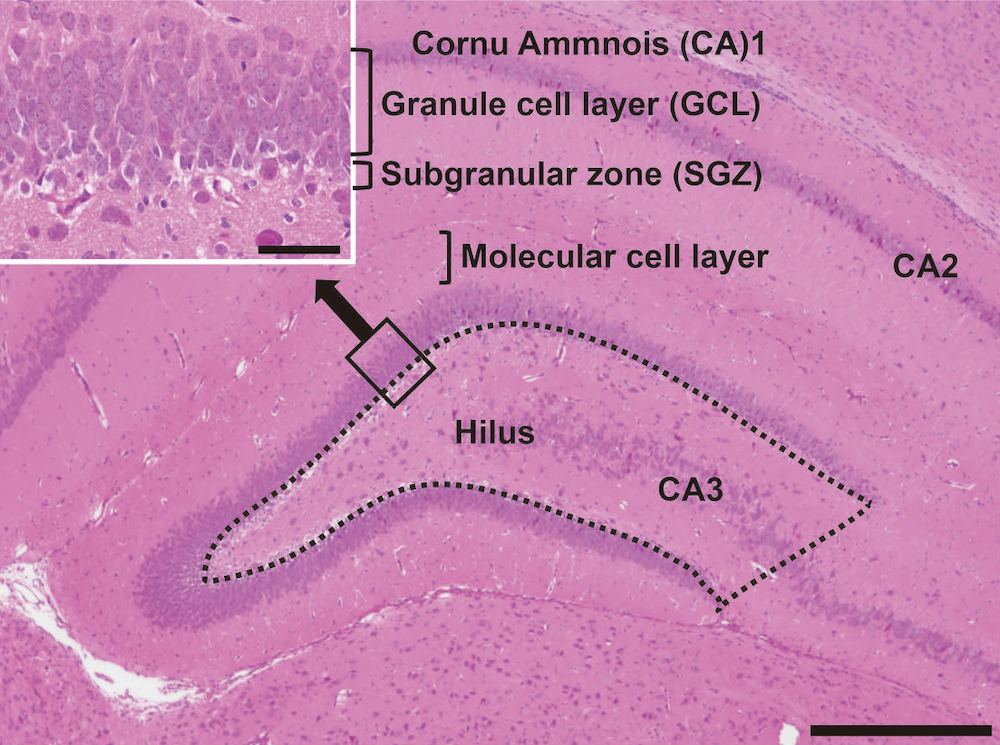
Ameliorating effect of postweaning exposure to antioxidant on disruption of hippocampal neurogenesis induced by developmental hypothyroidism in rats - Toxicologic Pathology

Expression of E-cadherin by CD8+ T cells promotes their invasion into biliary epithelial cells

A) Follicular hypertrophy in the thyroid in a female rat exposed to a

Mucosal viral infection induces a regulatory T cell activation phenotype distinct from tissue residency in mouse and human tissues - Mucosal Immunology

National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: IV. The 2020 Highly morbid forms report - Transplantation and Cellular Therapy, Official Publication of the
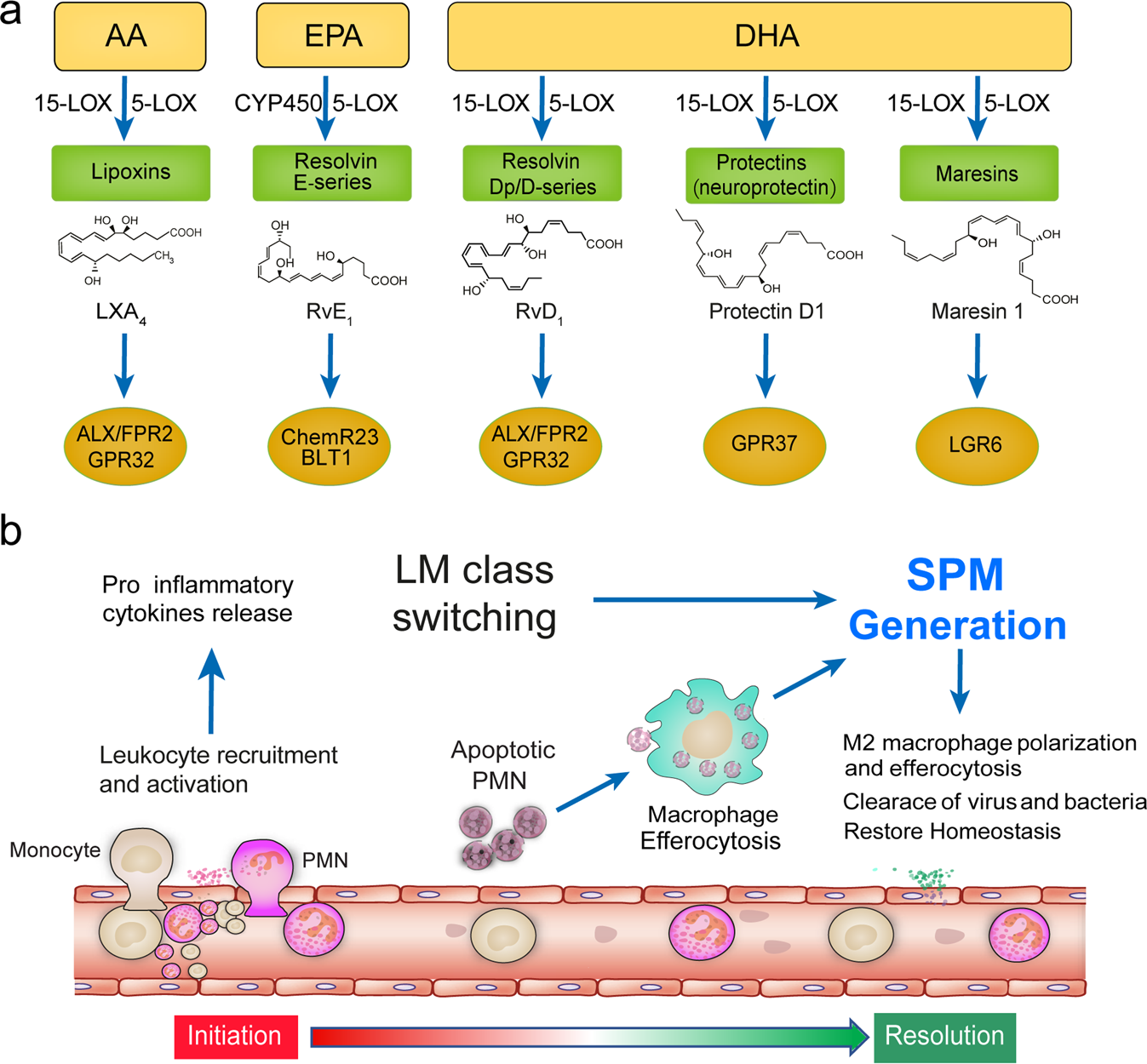
Inflammation and tumor progression: signaling pathways and targeted intervention

Oral mucosa - Hyperplasia, Squamous - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas
- Workwear Pants For Women In Autumn And Winter Plush And Thickened High Waisted Loose Fitting Harlan Leggings Loose Fitting High Waisted Casual Sports

- 2023 Autumn Winter Womens Westernized Cotton Harlan Winter Pants

- Thick-waisted Daddy Harlan Pipe Pants for Slimming

- Cookin' with Condley - Harlan Enterprise

- YCZDG Women's Autumn and Winter Plus Velvet Thick Jeans Were Thin

- Lululemon Wunder Under High-Rise Tight 28 *Full-On Luxtreme Manifesto - 20YR Manifesto Foil Dark Red - lulu fanatics

- Forearm Forklift 9.4 ft. L x 3 in. Moving Straps FF000012 - The Home Depot

- Up To 87% Off on Women Invisible Strapless Pus

- Skims Fits Everybody Lace Bodysuit - Skims Thong Bodysuit - Skims Body – Upside Threads

- Shyle Red Camouflage Print Cross Back Sports Bra
