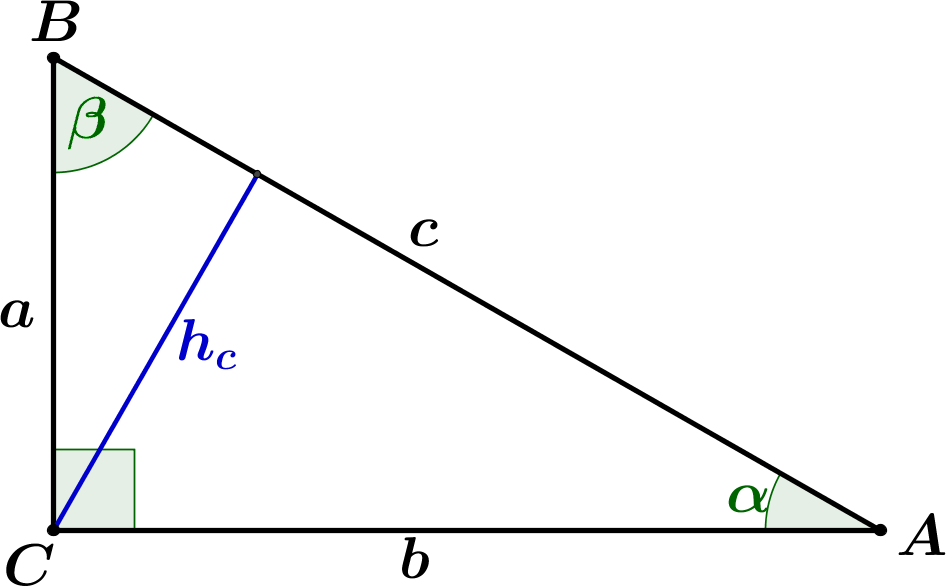
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the
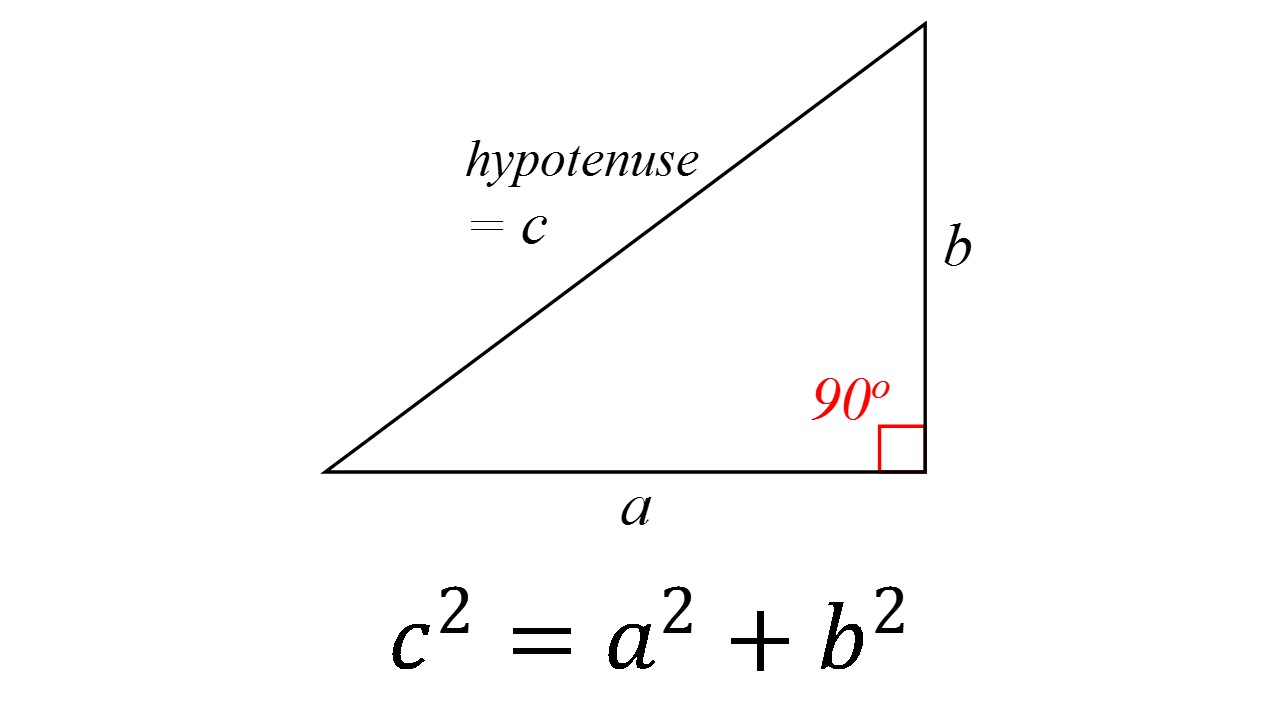
By A Mystery Man Writer
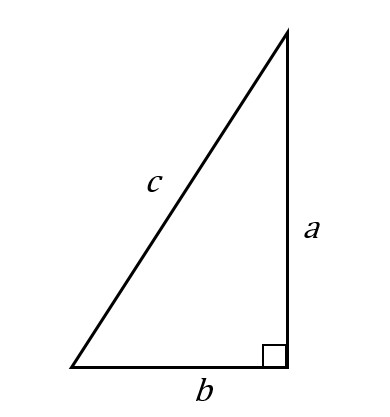
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.
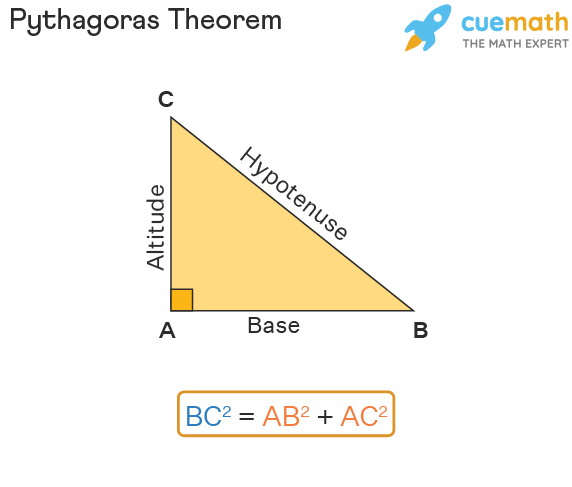
Pythagoras Theorem - Formula, Proof, Examples

How to Determine Whether a Triangle is a RIGHT Triangle
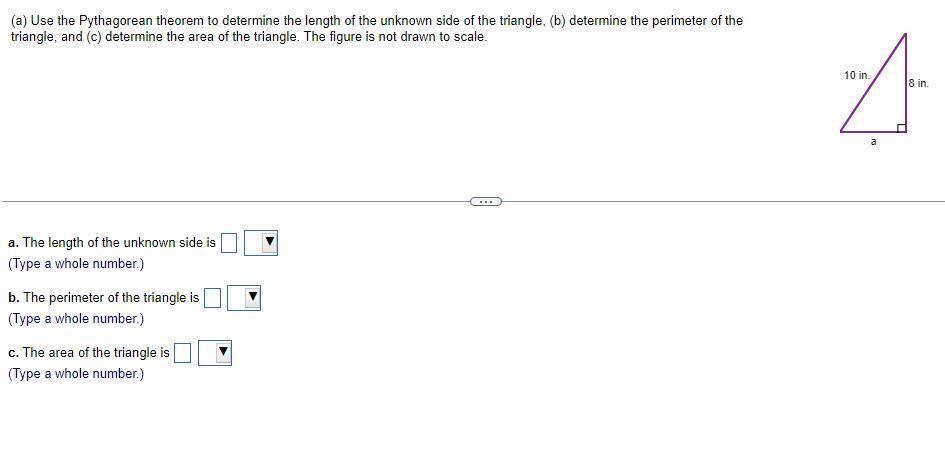
Solved (a) Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the

How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem: 12 Steps (with Pictures)

Pythagorean Theorem - MATH IN DEMAND
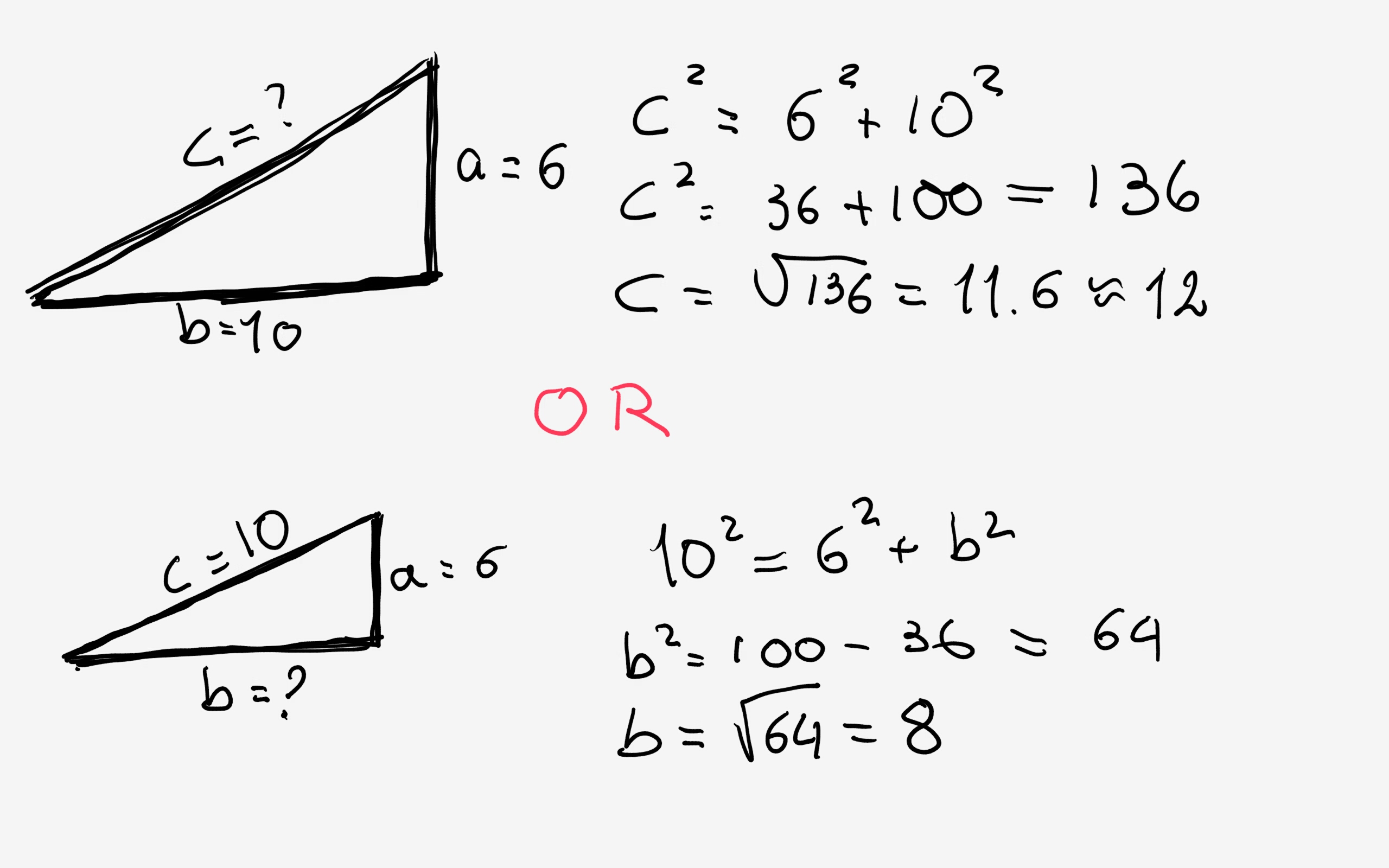
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the missing sides a = 6, b = 10?
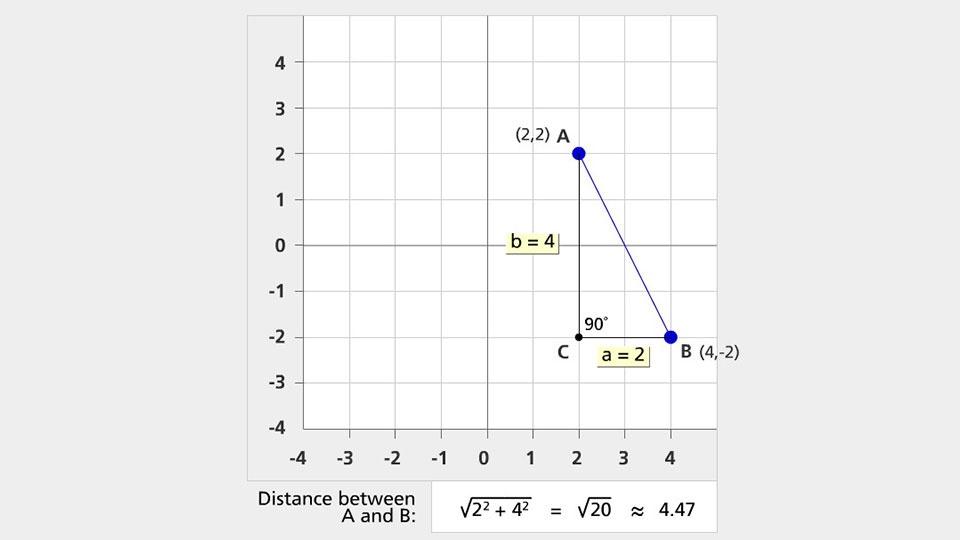
Calculating Distance Using the Pythagorean Theorem

Converse of Pythagorean Theorem - Expii
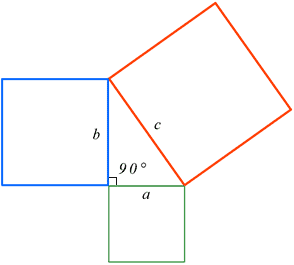
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator

Pythagorean Triples - Definition, Formula, Examples

4 Ways to Solve Pythagoras Theorem Questions - wikiHow

The Pythagorean Theorem
How to use the converse of the Pythagorean theorem to tell if a triangle is a right triangle - Quora
- adidas Brassière de sport adidas by Stella McCartney TruePace

- Nike Milwaukee Bucks Giannis Courtside Statement Edition Sweatshirt

- Nike Womens Swoosh Medium Support Sports Bra Purple XL

- Freya Swimwear Colour Crush Bikini Top

- SZXZYGS Underoutfit Bras for Women Woman Top Bra No Rims Underwears Base Vest Style Sports Base Underwears