Age acceleration differences in controls and subjects with the

By A Mystery Man Writer
Download scientific diagram | Age acceleration differences in controls and subjects with the ESRD. (a) DNAmAgeHannum 39 ; (b) DNAmAge 40 ; (c) IEAA 15,16 ; (d) EEAA 15,16 ; (e) DNAmPhenoAge 38 ; (f) DNAmGrimAge 41 . from publication: Accelerated epigenetic aging and inflammatory/immunological profile (ipAGE) in patients with chronic kidney disease | Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined by reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This failure can be related to a phenotype of accelerated aging. In this work we considered 76 subjects with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and 83 healthy controls. We evaluated | Chronic Kidney Disease, Epigenetics and Epigenomics | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Epigenetic age acceleration vs. chronological age in EPIC data. The

Motor disorder in Huntington's disease begins as a dysfunction in error feedback control

Lifespan changes in postural control

Accelerated epigenetic aging and inflammatory/immunological profile (ipAGE) in patients with chronic kidney disease
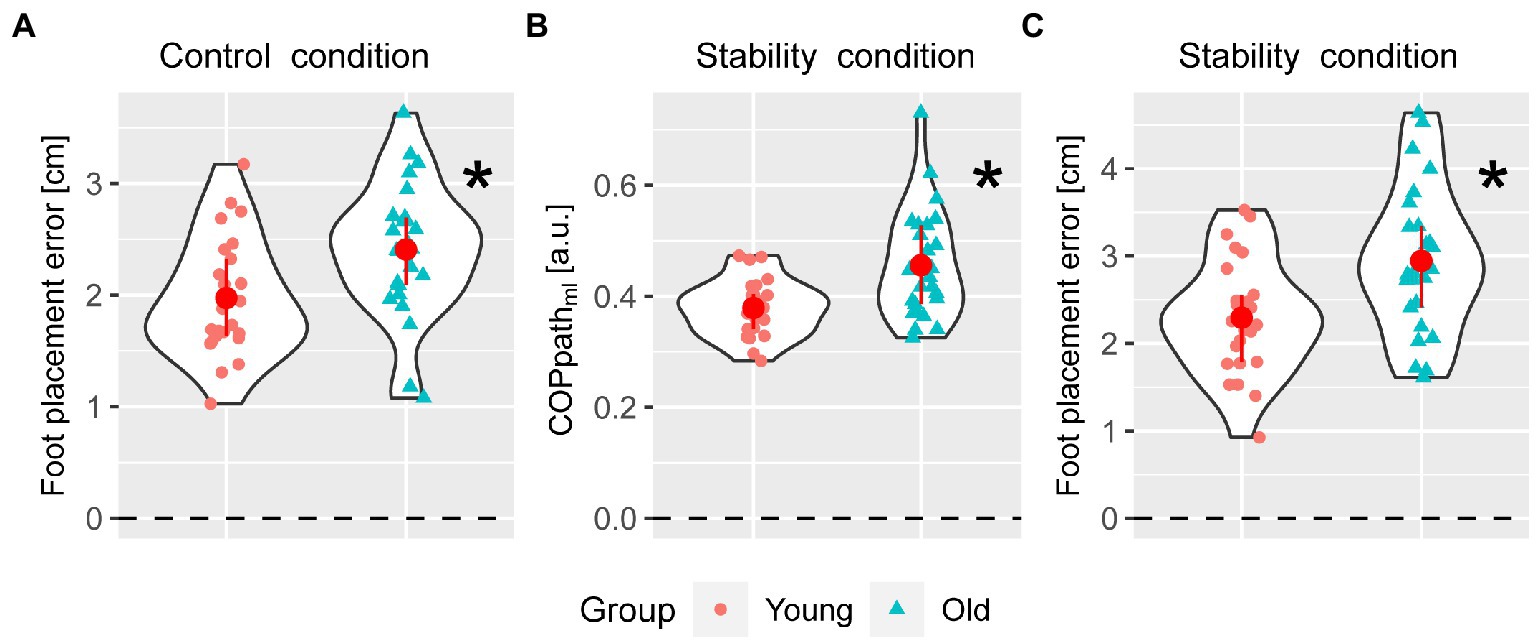
Frontiers Accuracy-speed-stability trade-offs in a targeted stepping task are similar in young and older adults
Cloud-based Air Force learning ecosystem to give control and “21st Century speed” to Airmen > Joint Base San Antonio > News

Deterministically Setting Hunting Speed Restrictions - Railway Age
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MIND-Left-Brain-Right-Brain-560318488e7b40c6a0093036ed4fd1f5.jpg)
What It Means to Be Left-Brained vs. Right-Brained

Variables in Research, Definition, Types & Examples - Lesson

50 Gross Motor Skills Examples (2024)
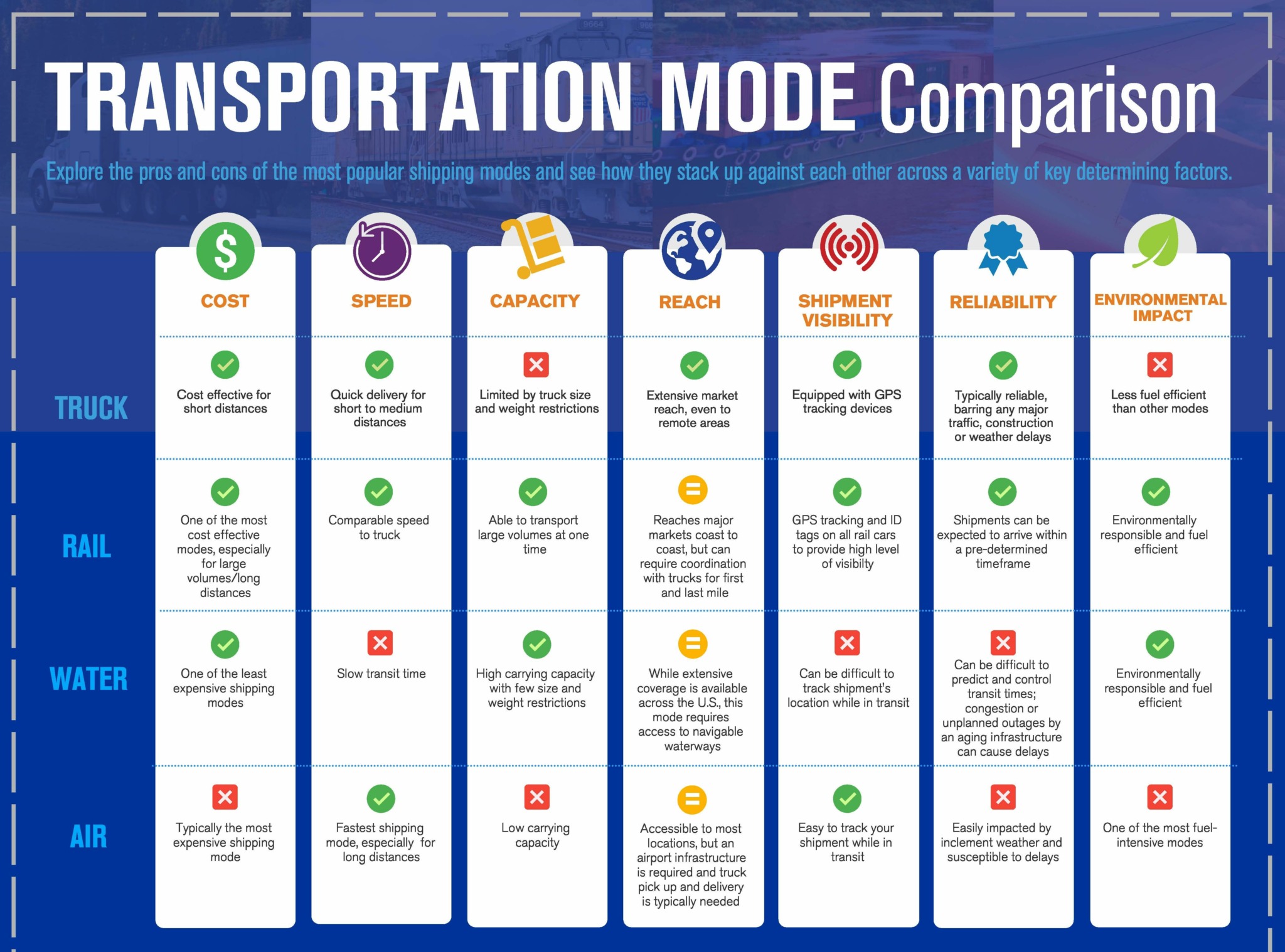
intermodal-graph-1 - Truck News

Table 1 from Heart rate recovery after exercise and neural regulation of heart rate variability in 30-40 year old female marathon runners.

Effects of age and thyroid status on speed of performance of individual

Causal effects of senescence through intrinsic epigenetic age acceleration on age-related diseases: a Mendelian randomization study
- HEATIT ET-21 Freeze Thermostatically Controlled Outlet on at 38F /Off at 50F

- Chantelle Womens C Magnifique Seamless Unlined

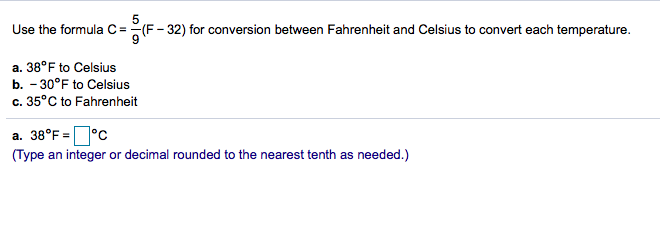
- Solved Use the formula C = CF (F-32) for conversion between
- Solved Which of the following is not a valid Float value?
- Doc says I (38F) should be taking (or consuming) 1000mg/day of

- Buy DAISY DEE Beige Cotton Blend Bra Online at Best Prices in India - JioMart.
)
- Vanilla Borderline Kink - Stretch Cotton Harness - Cupless Top - Cage Bra - Open Cup Bralette

- New Women’s Champion C9 Power Core Blue Floral Athletic Sports Bra Size XS

- Men's Washable Incontinence Underwear, Zorbies Absorbent Boxer Brief 1pk

- Ulla Popken Formuojantys Apatiniai Marškinėliai

