Comparison of acute single versus multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in radiographic characteristic and bone fragility, Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research
By A Mystery Man Writer
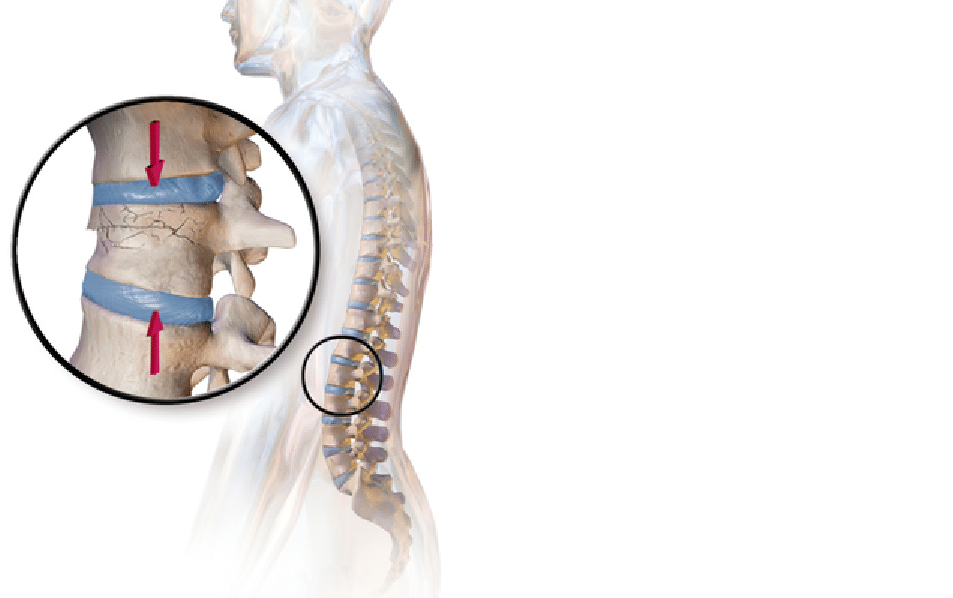
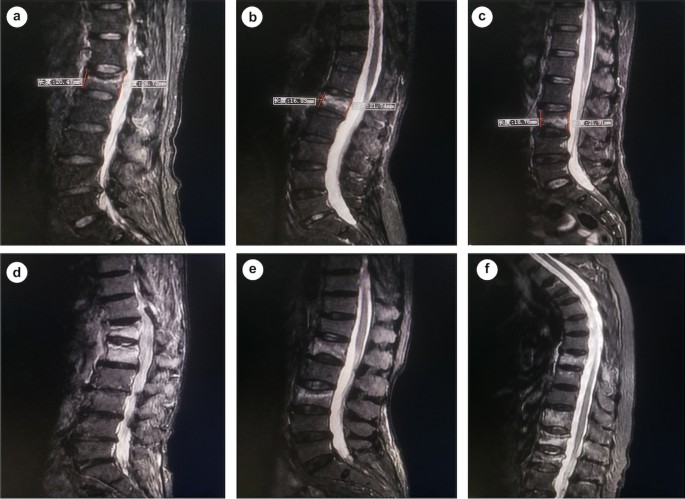
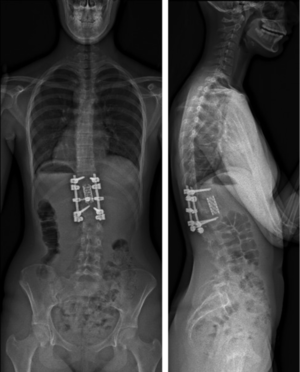
Background Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCF) are common in aged population with bone fragility. This study aimed to identify the radiographic and bone fragility characteristic of acute single and multiple OVCF. Methods OVCF patients hospitalized in a spine center between June 2016 and October 2020 were retrospectively studied. Demographics, comorbidity, bone mineral density, spine trauma, duration of pre-hospital back pain, anatomical location and distribution pattern of OVCF, extent of vertebral marrow edema, and degree of vertebral compression of patients with multi-segment vertebral fractures (MSVF) were summarized and compared to those with single segment vertebral fractures (SSVF). Results A total of 1182 patients with 1530 acute fractured vertebrae were included. There were 944 SSVF (79.9%) and 238 MSVF (20.1%) simultaneously involving two (MSVF-2) or three and more vertebra (MSVF-3/m). The Female-Male ratio was 4.4 and differed not significantly between SSVF and MSVF. Females in SSVF were younger than males while MSVF-2 tended to occur in older females. L1, T12, and L2 were the three most frequently fractured vertebra and MSVF involved more vertebra in thoracic and lumbar spine. 31.1% in MSVF-2 and 83.1% in MSVF-3/m had at least two vertebral fractures in adjacent. The fractured thoracolumbar vertebra in MSVF was less compressed than that in SSVF. Apparent spine trauma was reported by 61.4% of SSVF, 44.1% of MSVF-2, and 36.3% of MSVF-3/m, while early hospitalization with pre-hospital back pain ≤ 1 week was 58.9% in SSVF, 45.3% in MSVF-2, and 25.9% in MSVF-3/m. Only females aged 70–80 years old in MSVF-3/m showed lower baseline bone mineral density than in MSVF-2 and SSVF. MSVF were not associated with increased comorbidity of hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, and chronic pulmonary disease. Conclusions 20% of acute OVCF can involve multiple vertebra without significant spine trauma or lower baseline bone mineral density. Multiple OVCF tend to occur in adjacent vertebra with less thoracolumbar vertebral compression but longer duration of pre-hospital back pain.
Vertebral Collapse—Benign or Malignant
Vertebral Fractures in Children and Adolescents - Physiopedia
Osteopenia UW Radiology

Spinal Cord Injuries: Traumatic, Nursing CEU
Osteoporotic Fractures - Treatment and Rehabilitation - Neuroaxis

Guidance to Bone Morbidity in Children and Adolescents Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation - Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation

Distribution of single and multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression

Pathologic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Diagnosis and Management

AOT Osteo Fx Care book sample by AO Foundation - Issuu
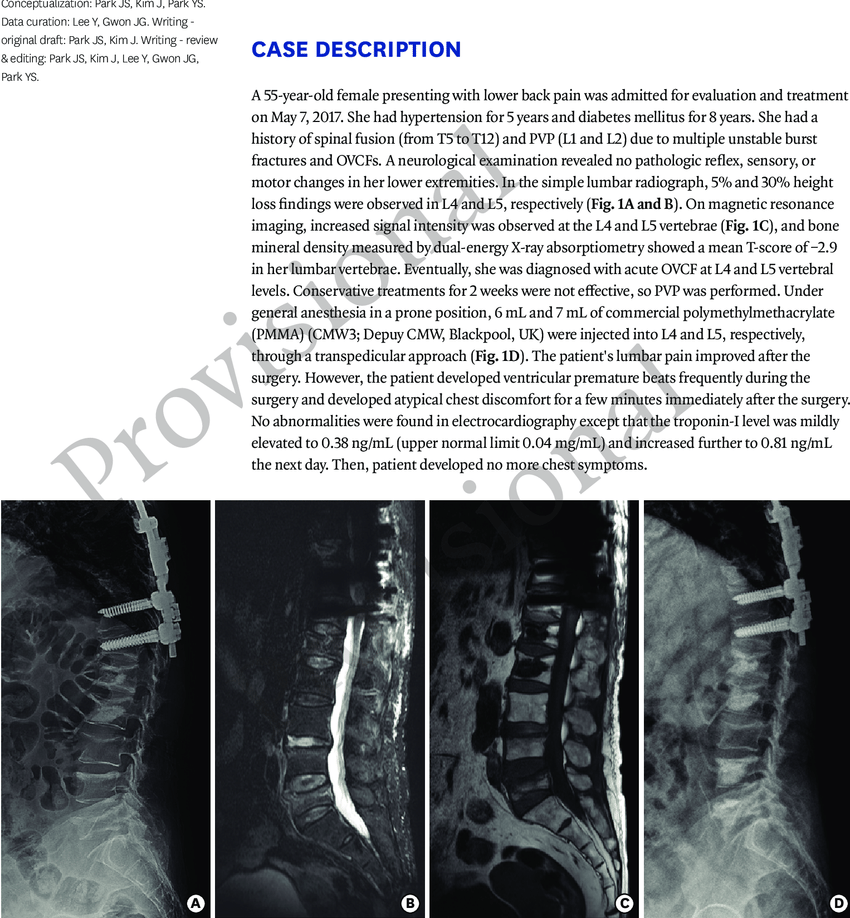
The diagnosis and treatment of acute osteoporotic vertebral compression

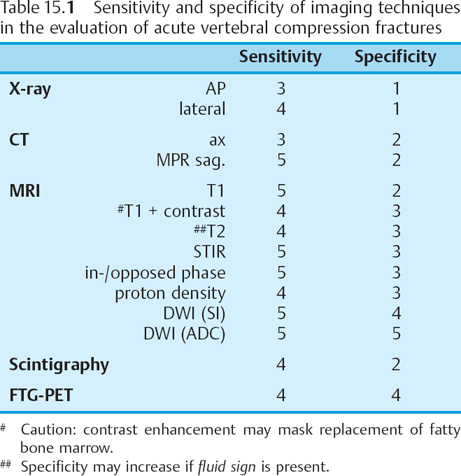
Imaging in Osteoporosis and Paget's disease
Osteoporosis Workup: Approach Considerations, Laboratory Studies, Biochemical Markers of Bone Turnover

Comparison of acute single versus multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in radiographic characteristic and bone fragility, Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research
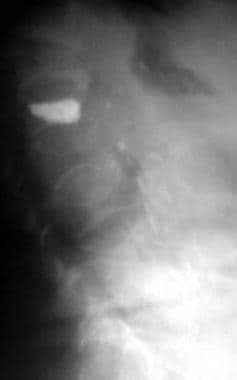
Osteoporosis: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology
- Everything You Should Know about Spinal Compression Fractures - Colorado Pain Care
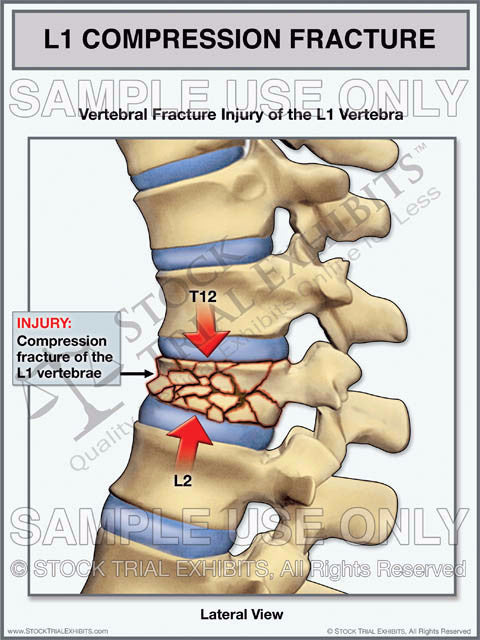
- L1 Vertebra Compression Fracture Trial Exhibit – Stock Trial Exhibits
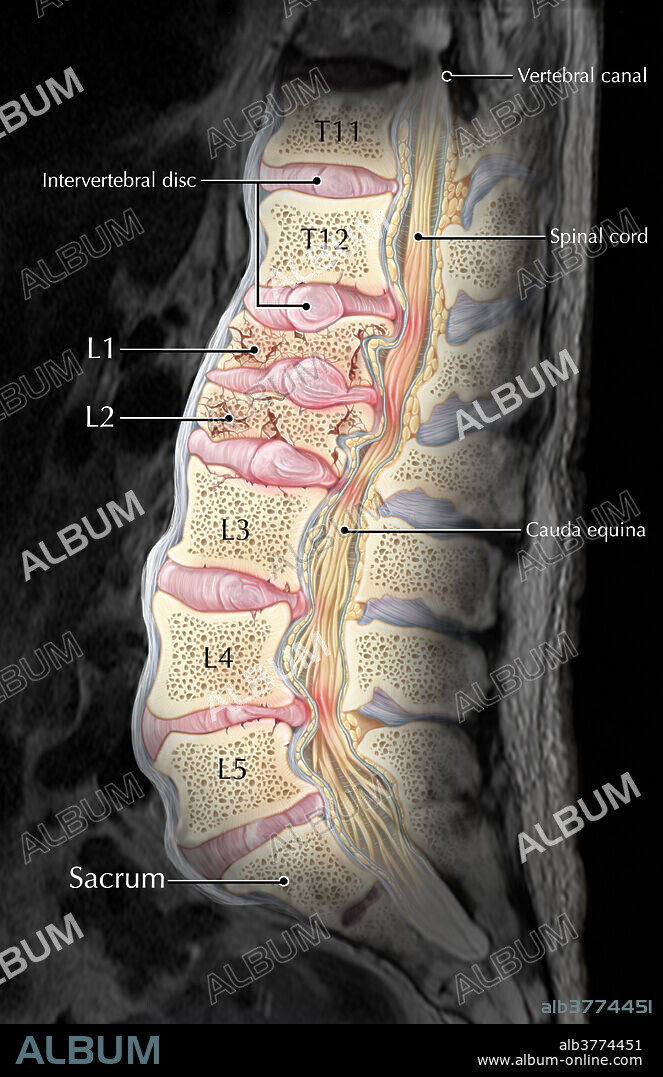
- Lumbar Compression Fracture, Illustration - Album alb3774451
- Vertebral Body Fractures and Vertebral Compression Fractures

- Vertebral Compression Fracture: Definition - Spine Info